Skin

Skin
Rosacea: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatments
8 minutes read | 2 Apr 24

Ever wondered why your cheeks flush crimson at the slightest trigger? If so, you're not alone. The causes of rosacea, that persistent redness and those frustrating flare-ups, often leave us puzzled. In this guide, we're diving headfirst into the world of rosacea, unravelling its mysteries in simple terms. Discover proven treatment approaches, lifestyle tweaks, and expert insights that can help you take charge of your skin's well-being. Let's demystify the journey to calmer, healthier skin together.
What is Rosacea?
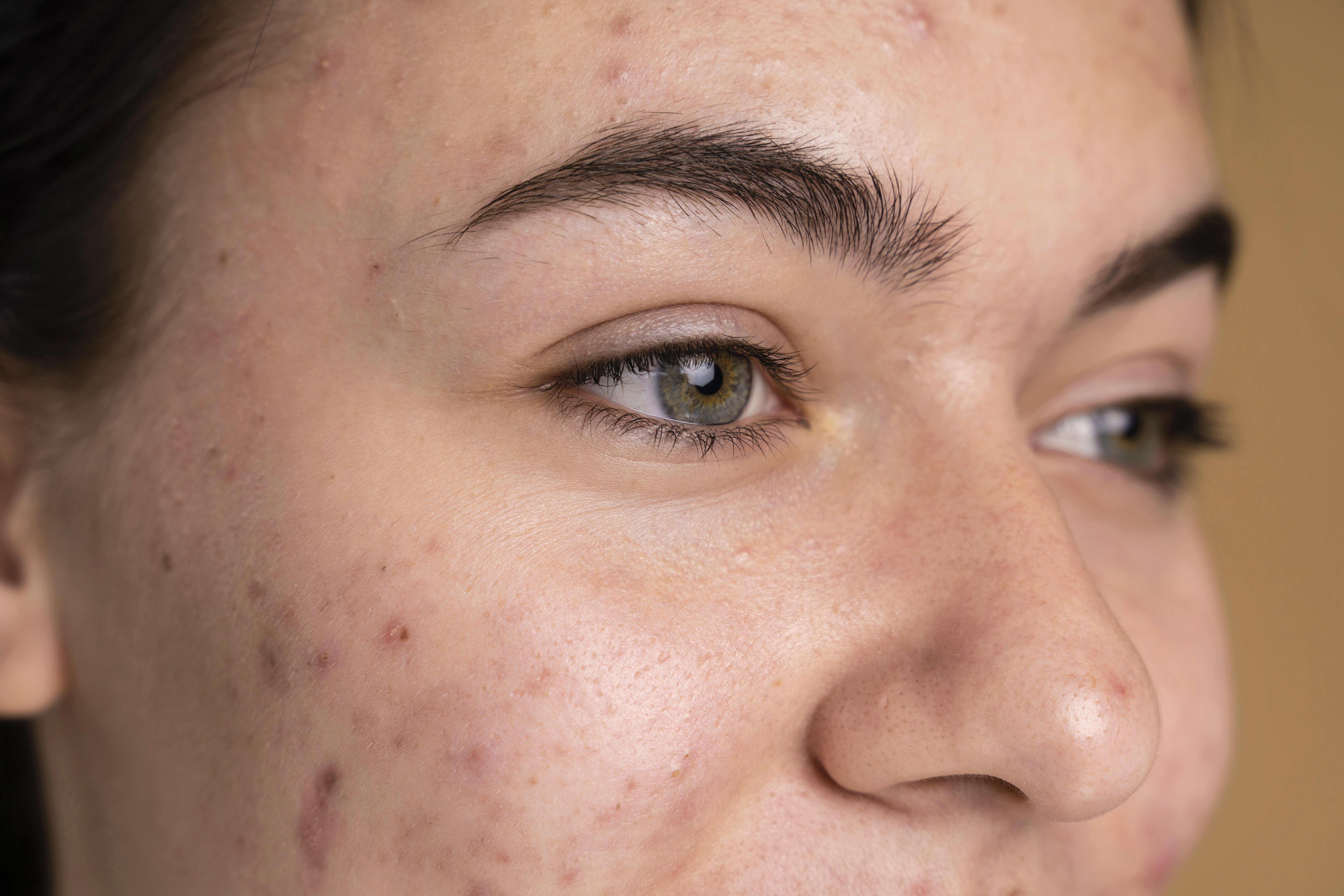
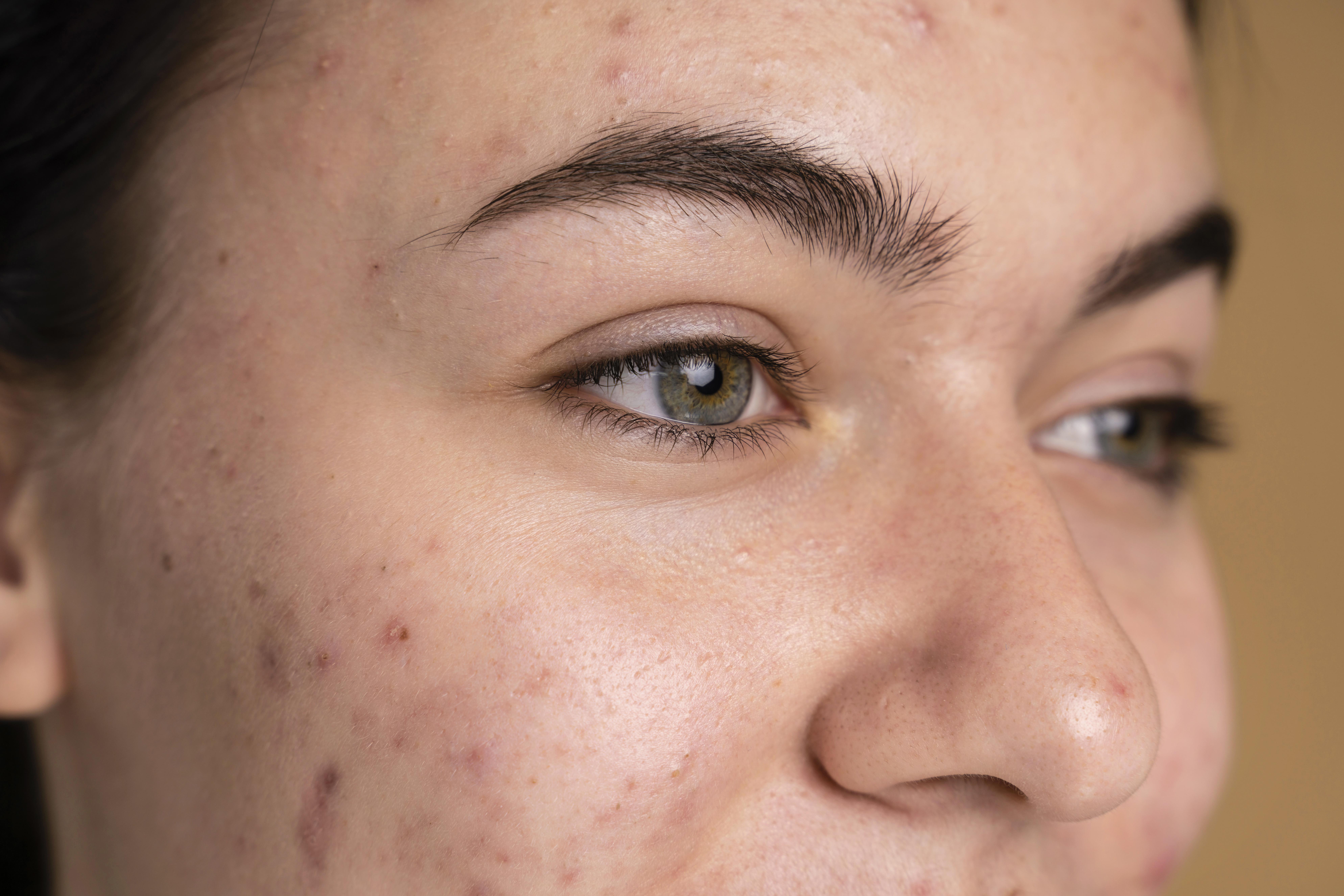
Rosacea is a common yet perplexing skin condition characterised by persistent redness, visible blood vessels, and occasional flare-ups of pimple-like bumps on the face. It often begins subtly, with a tendency to blush more than others. This condition primarily affects the central face, including the forehead, nose, and cheeks. Beyond its visible aspects, rosacea can lead to discomfort, stinging sensations, and a feeling of heat on the skin. It's essential to recognise the signs early, as untreated rosacea can worsen over time. Despite lacking a cure, various proven treatments and lifestyle adjustments exist to manage and alleviate the symptoms, providing individuals with a pathway to a more comfortable and confident life.
What are the Symptoms of Rosacea?
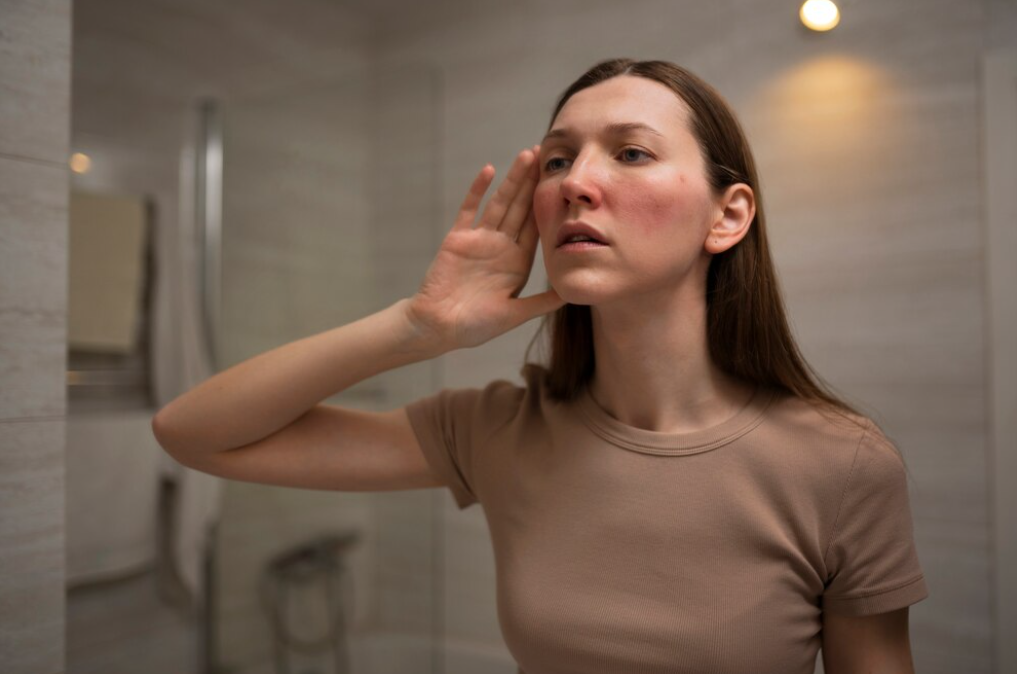
Rosacea manifests in a spectrum of symptoms, making it essential to recognise its varied expressions for effective management. From persistent redness to occasional flare-ups, understanding the signs is crucial.
Symptoms of Rosacea
Facial Redness:
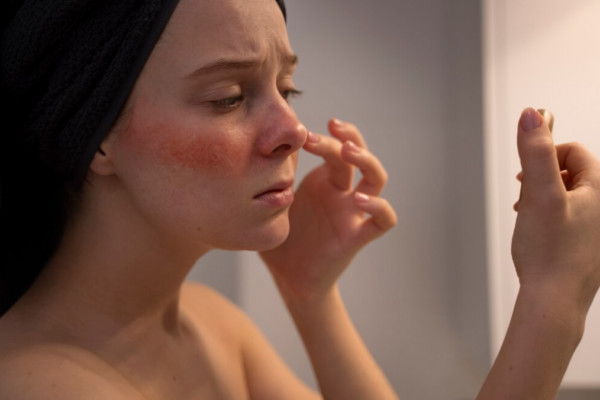

One of the hallmark signs is persistent redness on the face, particularly in the central regions such as the forehead, nose, and cheeks. The skin may appear as if it's constantly blushing, and this redness can be exacerbated by triggers like heat, spicy foods, or emotional stress.
Visible Blood Vessels:
Small blood vessels, known as telangiectasia, become visible on the skin's surface. These dilated capillaries contribute to the overall redness and can create a network of fine, red lines.
Pimple-like Bumps:
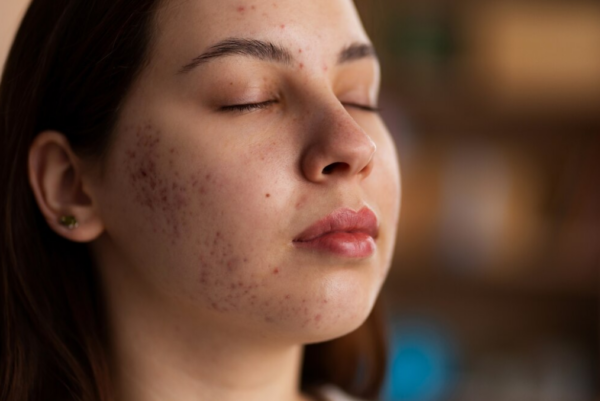

Raised, red bumps resembling acne may develop. These bumps, known as papules and pustules, can contain pus and might be mistaken for traditional acne. Unlike acne, however, they are not caused by clogged pores.
Eye Irritation:
Ocular rosacea can cause eye-related symptoms, including a gritty or burning sensation, dryness, redness, and sensitivity to light. In some cases, it can lead to more severe eye issues if left untreated.
Burning or Stinging:
Individuals with rosacea may experience a persistent sensation of heat, burning, or stinging on the affected areas of their face. This discomfort can be triggered by various factors, including environmental conditions and certain skincare products.
Swelling:
Facial swelling, particularly around the nose, may occur. This swelling can contribute to changes in the skin's texture and appearance.
Sensitive Skin:

Rosacea often makes the skin more sensitive, leading to increased reactions to skincare products, environmental factors, or even temperature changes.
Enlarged Nose (Rhinophyma):
In rare cases, particularly if rosacea is left untreated, there may be thickening and enlargement of the nose. This condition, known as rhinophyma, is more common in men and can significantly impact the nose's shape and appearance.
What are the Causes of Rosacea?
Understanding the elusive causes of rosacea is key to managing and preventing its persistent symptoms. While the exact triggers remain unclear, several factors are believed to contribute to the development and exacerbation of this skin condition.
Genetics:
There's a significant genetic component to rosacea. If someone in your family has or had rosacea, you may be more prone to developing it. This genetic predisposition suggests that certain individuals may inherit a susceptibility to the condition.
Abnormal Immune Response:
Rosacea is associated with an abnormal immune system response, where the body's defence mechanisms mistakenly target the skin, leading to chronic inflammation. This inflammation manifests as the characteristic redness, swelling, and other symptoms seen in rosacea.
Dermatitis Mite (Demodex):
An overgrowth of the skin mite Demodex folliculorum is often found in higher numbers on the skin of individuals with rosacea. While their precise role isn't fully understood, their presence may contribute to the inflammatory response, potentially triggering or exacerbating rosacea symptoms.
Blood Vessel Abnormalities:
Rosacea involves abnormalities in the blood vessels close to the skin's surface. These vessels tend to dilate more easily than normal, contributing to the persistent redness seen in affected individuals.
Environmental Triggers:

Various environmental factors can provoke or worsen symptoms of rosacea. Sun exposure, extreme temperatures, wind, spicy foods, hot beverages, and alcohol are common triggers. Identifying and avoiding these triggers can be crucial in managing and preventing flare-ups.
Microorganisms:
The presence of certain microorganisms, such as Helicobacter pylori bacteria in the digestive system, has been investigated as a potential factor in rosacea. Research is ongoing to establish a definitive connection and understand the role of these microorganisms in the development of the condition.
Skin Barrier Dysfunction:

Impairment in the skin's natural barrier function may render it more susceptible to irritation and inflammation. This dysfunction can contribute to the development of rosacea and make the skin more reactive to various triggers.
Use of Topical Steroids:
Prolonged use of topical steroids on the face can lead to a specific form of rosacea known as steroid-induced rosacea. Abruptly stopping these medications may also trigger a flare-up, highlighting the importance of judicious use of topical steroids under medical supervision.
How to Get Rid of Rosacea Permanently?
Addressing rosacea involves a combination of lifestyle changes, skincare, and in some cases, professional treatments. While there isn't a guaranteed permanent solution, a proactive approach can significantly reduce symptoms and improve overall skin health.
General Treatments of Rosacea
Skincare Routine:

Adopting a gentle skincare routine is pivotal. Choose fragrance-free, hypoallergenic products suitable for sensitive skin. Avoid abrasive cleansers, opting for mild, hydrating options to maintain skin barrier health.
Sun Protection:
Shielding the skin from harmful UV rays is crucial. Regular use of broad-spectrum sunscreen with at least SPF 30 helps prevent flare-ups triggered by sun exposure. Additionally, wearing hats and seeking shade contributes to overall sun protection.
Dietary Adjustments:

Identifying and avoiding trigger foods plays a significant role in managing rosacea symptoms. Spicy foods, hot beverages, and alcohol are common triggers. An anti-inflammatory diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and omega-3 fatty acids may also be beneficial.
Stress Management:
Stress is a known trigger for rosacea flare-ups. Incorporating stress reduction techniques into daily life, such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, or yoga, can help minimise stress-related skin reactions.
Antibiotics (Oral or Topical):
Antibiotics, either in oral or topical form, are commonly prescribed to manage inflammatory symptoms of rosacea. Oral antibiotics like doxycycline or tetracycline may help reduce redness and inflammation, while topical antibiotics such as metronidazole can be applied directly to the affected skin.
Topical Treatments:
Prescription topicals like azelaic acid or metronidazole gel can be effective in controlling redness and inflammation associated with rosacea. These products work by reducing inflammation, inhibiting the growth of certain skin bacteria, and improving uneven skin texture.
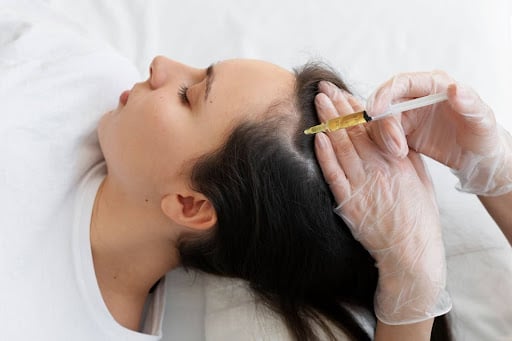
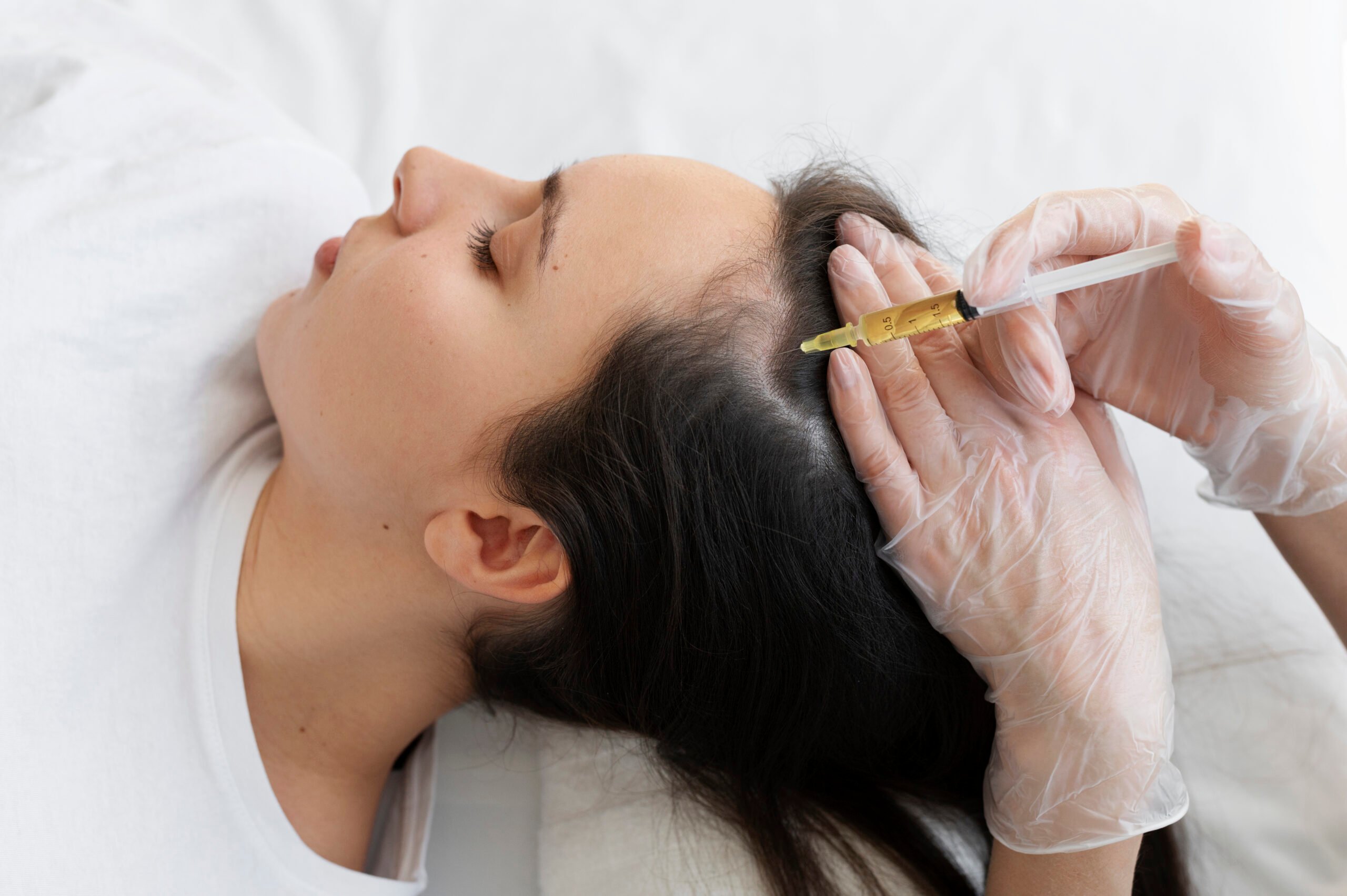
Professional Treatments of Rosacea at Bodycraft Clinic
Q-Switch Laser Treatment:
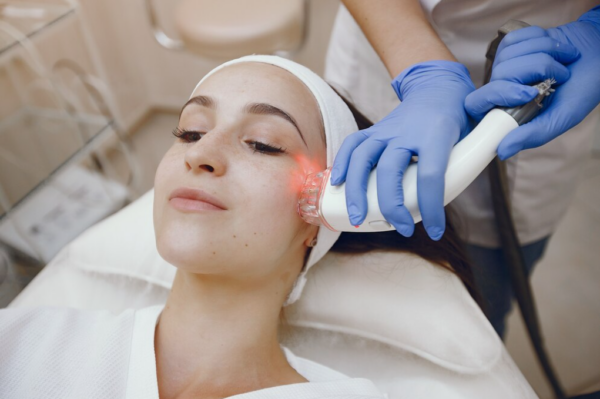
The Q-Switch Laser is a high-intensity laser that targets pigmentation. It breaks down pigments, aiding the body's natural elimination process. This treatment is versatile, addressing uneven skin tone, lightening pigmentation, and reducing the appearance of acne scars. It can be applied to various areas like the face, neck, chest, and back.
Hydra-Medi Facial:
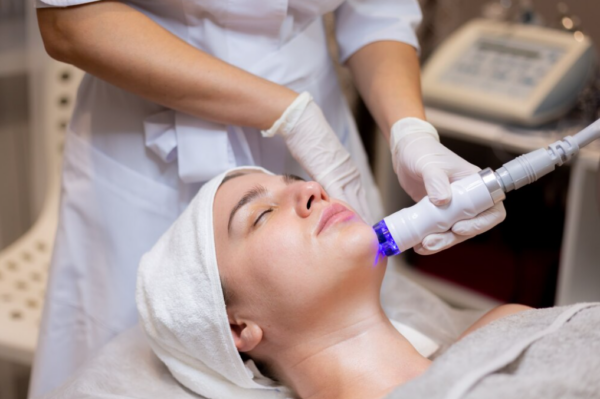
This treatment combines natural oxygenation, Tripollar Radio Frequency, and Ultrasound in a three-step process. First, exfoliation removes dead cells. Then, infusion cleanses and nourishes the skin with active ingredients. Finally, oxygenation optimises the absorption of these ingredients, promoting skin healing from within. The Hydra-Medi Facial treatment is effective for a range of skin concerns, providing immediate visible improvement and long-term rejuvenation.
Profhilo Treatment:
Profhilo is an injectable treatment with hyaluronic acid, a natural skin component. It stimulates collagen and elastin production, addressing issues like sagging, wrinkles, and dullness. The treatment helps improve skin texture and elasticity, resulting in an overall rejuvenated appearance. It is particularly popular for its hydration-boosting properties and is suitable for various areas of the face.
These professional treatments, under the guidance and care of our doctors at Bodycraft clinic, have the potential to complement the holistic approach to managing rosacea, addressing both the underlying inflammation and visible symptoms.
When to See a Dermatologist?
It's crucial to consult a dermatologist if you suspect or observe persistent facial redness, visible blood vessels, or acne-like bumps, as these may indicate rosacea. Early intervention enhances effective management. Additionally, seek dermatological advice if lifestyle adjustments and over-the-counter remedies prove insufficient. Dermatologists can provide a definitive diagnosis, identify triggers, and tailor a treatment plan, including prescription medications and professional interventions, to alleviate symptoms. Regular check-ups with a dermatologist ensure ongoing support and adjustments to the treatment plan, promoting long-term skin health. If you experience eye irritation or notice changes in your skin, consulting a dermatologist promptly is essential.
The Takeaway
In essence, managing rosacea involves a mix of gentle skincare, lifestyle tweaks, and, if needed, professional treatments. While there's no one-size-fits-all solution, understanding triggers and early intervention are key. Regular consultations with a dermatologist can guide personalised care. From sunscreen habits to advanced treatments, taking steps today ensures a brighter, calmer skin tomorrow. Remember, it's not just about getting rid of rosacea; it's about nurturing your skin's health for the long run.
FAQs around Rosacea
1. What does rosacea look like?
Rosacea appears as persistent redness on the face, often on the central regions like the nose and cheeks. It may involve visible blood vessels and acne-like bumps, contributing to an overall flushed or blushed appearance.
2. Is rosacea itchy?
Typically, rosacea is not associated with itching. However, some individuals may experience a burning or stinging sensation, but itchiness is not a common symptom.
3. Is rosacea an autoimmune disease?
No, rosacea is not an autoimmune disease. It's a chronic skin condition characterised by inflammation, primarily affecting the face.
4. Is rosacea contagious?
No, rosacea is not contagious. It doesn't spread through contact or airborne means. It's a skin condition influenced by various factors, including genetics and environmental triggers.
5. Does rosacea get worse with age?
In some cases, yes. Rosacea tends to worsen over time if left untreated. However, proper management, lifestyle adjustments, and professional treatments can control and alleviate symptoms effectively.
6. Does rosacea go away?
While there's no cure for rosacea, it can be effectively managed. With the right treatments and lifestyle adjustments, symptoms can be controlled, providing long-term relief.
7. Is rosacea genetic?
Yes, there is a genetic component to rosacea. If someone in your family has or had rosacea, you may be more predisposed to developing the condition. However, environmental factors also play a significant role.
Related categories
Get a complimentary consultation today. Book now



































.png)
























-1.png)